On Day 28, we move into the world of Automation. After a short New Year’s break… it is time to stop manually running tests and checking for bugs. Today, we implement CI/CD (Continuous Integration / Continuous Deployment) using GitHub Actions.
This is the “pro-tier” transition. From now on, every time you push code to GitHub, a virtual machine will spin up, install your dependencies with uv, and run your entire test suite to make sure you didn’t break anything. So, today, we ensure that no broken code ever makes it to production.
1. What is CI/CD?
- Continuous Integration (CI): Automatically building and testing your code every time you make a change.
- Continuous Deployment (CD): Automatically shipping that code to your server once the tests pass.
2. The Power of uv in CI
One of the biggest pain points in CI is the time it takes to install dependencies. Using the astral-sh/setup-uv action, we can install our environment in seconds rather than minutes.
3. Creating the Workflow
Create a file at .github/workflows/test.yml:
name: Python Testing
on: [push, pull_request]
jobs:
test:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- uses: actions/checkout@v4
- name: Install uv
uses: astral-sh/setup-uv@v5
with:
enable-cache: true # Supercharges subsequent runs!
- name: Set up Python
run: uv python install
- name: Install dependencies
run: uv sync
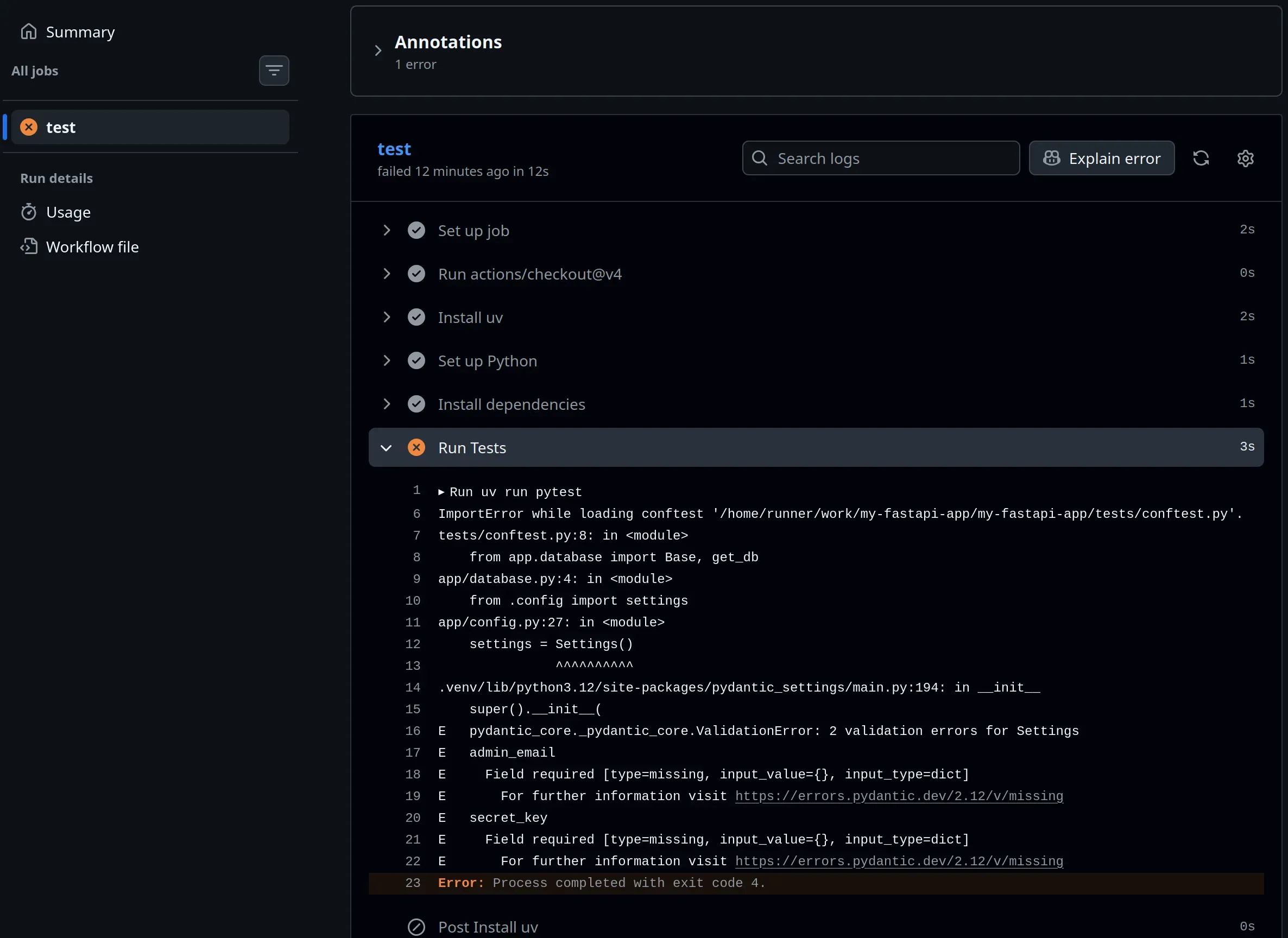
- name: Run Tests
run: uv run pytest
4. Configuring Pytest for Discoverability
For pytest to find your app module correctly in the CI environment (and locally), you need to ensure your root directory is in the PYTHONPATH. The most robust way to do this is by adding a configuration block to your pyproject.toml:
[tool.pytest.ini_options]
pythonpath = ["."]
testpaths = ["tests"]5. Why the Cache Matters?
In the YAML above, enable-cache: true tells GitHub to “remember” your uv dependencies. This means that if your uv.lock hasn’t changed, GitHub doesn’t need to download anything—it just pulls from the cache.
🛠️ Implementation Checklist
- Created the
.github/workflowsdirectory. - Wrote the
test.ymlfile using thesetup-uvaction. - Configured
pytestinpyproject.tomlfor module discovery. - Pushed the code to GitHub and watched the “Actions” tab turn green.
- Purposely broke a test and verified that GitHub blocked the “Merge” (proving the safety net works!).
- Verified that my Global Exception Handler logic is still being tested properly in the cloud environment.
📚 Resources
- GitHub Docs: Quickstart for GitHub Actions
- uv Docs: Using uv in GitHub Actions
- Book: FastAPI: Modern Python Web Development (Chapter 13: Deployment) - Only some general information about CI/CD.

