Categories
Tags
30days AI ai backend blog blogging booking burnout career chatbot cms coding design development devops django docker email express fastapi flight Flight Booking System full stack full-stack gmail GPT-3 interviews journey LinkedIn MERN mongodb NextJS nextjs notion OpenAI openai planning portfolio programming project python react ReactJS search sendgrid smtp software software development tailwind
239 words
1 minutes
Day 13 of 30 Days of FastAPI - Transitioning to SQLAlchemy — Beyond the JSON File
Today, we replace our local db.json with a SQLite database using SQLAlchemy.
1. What is an ORM?
An Object-Relational Mapper (ORM) allows you to interact with your database using Python classes instead of writing raw SQL (like SELECT * FROM items).
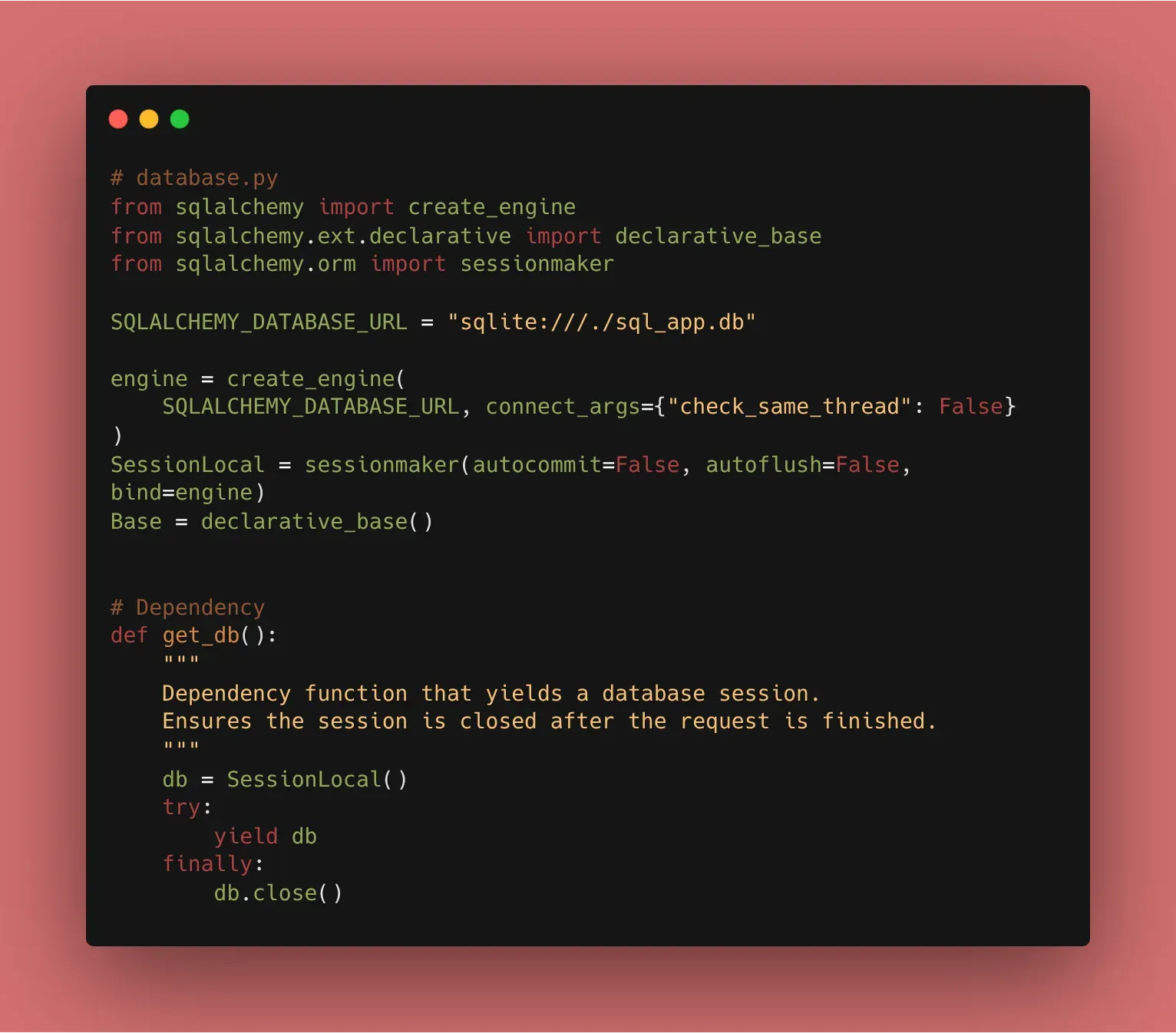
2. Setting Up the Engine
First, we need to install the tools. With uv, it’s a single command:
uv add sqlalchemy
Then, we create the database.py file to handle our connection:
from sqlalchemy import create_engine
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy.orm import sessionmaker
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URL = "sqlite:///./sql_app.db"
engine = create_engine(
SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URL, connect_args={"check_same_thread": False}
)
SessionLocal = sessionmaker(autocommit=False, autoflush=False, bind=engine)
Base = declarative_base()
3. Creating the Database Model
This looks similar to a Pydantic model, but it serves a different purpose: it tells the database how to create the table.
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, String, Float
from .database import Base
class ItemDB(Base):
__tablename__ = "items"
id = Column(Integer, primary_key=True, index=True)
name = Column(String, index=True)
price = Column(Float)
description = Column(String, nullable=True)
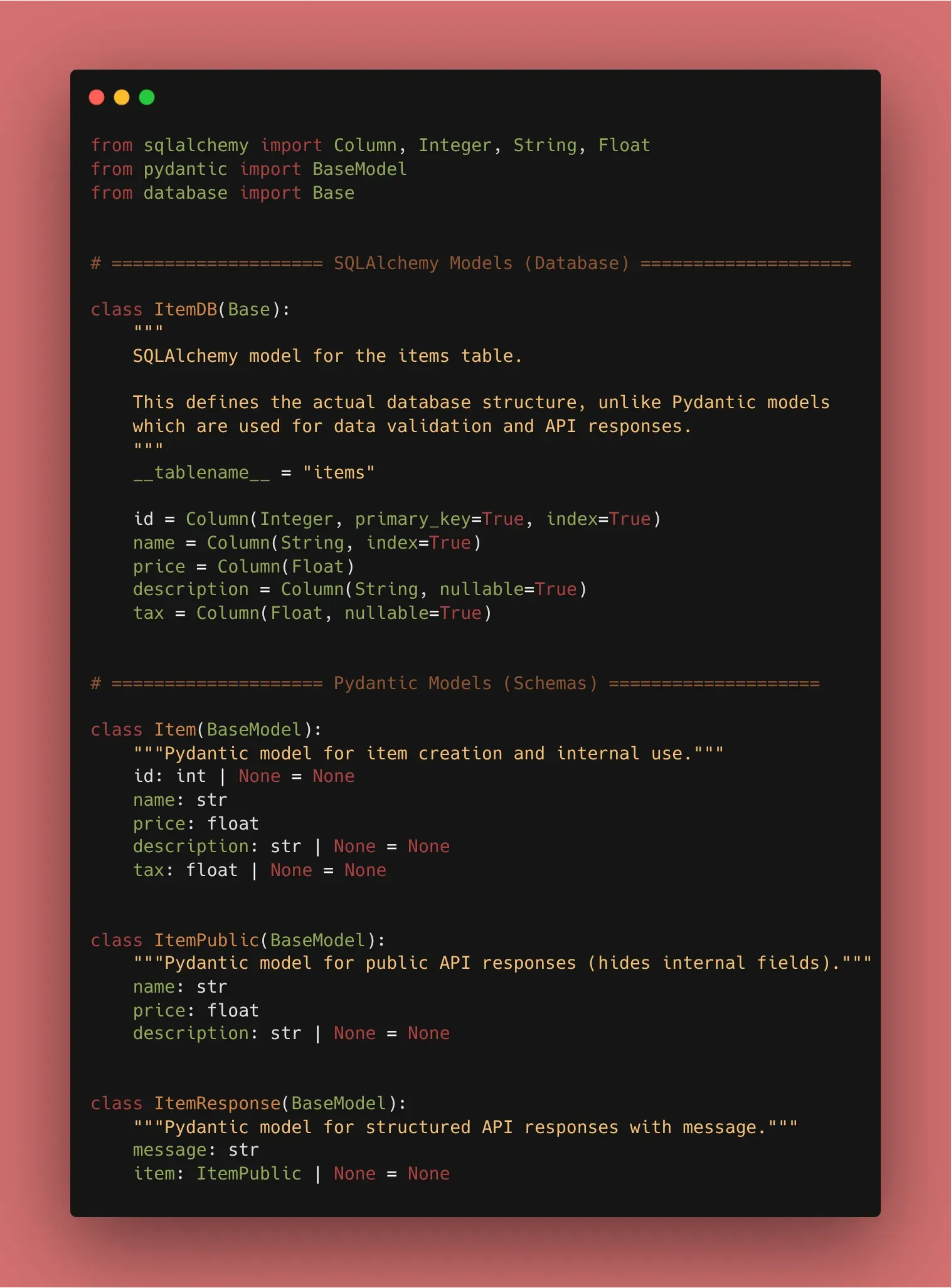
4. Why the separation?
Now we have three types of models:
- SQLAlchemy Models: For the Database structure.
- Pydantic Models (Schemas): For data validation and API responses.
- Response Models: For what the user actually sees.
This separation keeps your code clean and prevents your database structure from being leaked to the public!
🛠️ Implementation Checklist
- Installed
sqlalchemyusing uv. - Configured the
engineandSessionLocal. - Defined the
Baseand theItemDBmodel. - Verified that
sql_app.dbis created when the app starts.
📚 Resources
- Official Docs: FastAPI SQL (Relational) Databases
- Book: FastAPI: Modern Python Web Development (Chapter 6: Working with Databases).
Day 13 of 30 Days of FastAPI - Transitioning to SQLAlchemy — Beyond the JSON File
https://beyond400.vercel.app/posts/fastapi-13/
